https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/scrutiny-of-radioactive-waste-management-directorates-rwmd-work
This is a joint publication by the Environment Agency and the Office for Nuclear Regulation to inform others about our oversight of Radioactive Waste Management Limited’s (RWM) work relating to geological disposal of radioactive waste. Prior to the start of formal regulation, we have established agreements with RWM to provide regulatory advice in relation to geological disposal. The regulators are working together to make sure that any future geological disposal facility (GDF) will meet our high standards for environmental protection, safety, security, radioactive materials transport and safeguards.
There is however nothing addressing security issues in this report, except a footnote, which itself refers to an 80 page ONR generic nuclear facilities licensing document, which contains these two paras alone on security. This is totally inadequate, especially as the ONR has a dual security and safety regulatory mission:
Security
39 ONR’s security team has responsibility for regulating security for the civil nuclear industry and enforcing the Nuclear Industries Security Regulations 2003 (NISR). ONR’s security team has issued the National Objectives, Requirements and Model Standards (NORMS) document that sets out a series of security objectives and model standards which provide a possible solution to meet these
objectives. It approves and inspects against the duty holders’ security arrangements. These are described in Nuclear Site Security Plans and/or Construction Site Security Plans.
40 ONR’s security team’s remit also includes management of sensitive nuclear information and the transport of nuclear material both within the UK and overseas on UK flagged vessels. In addition, ONR approves and inspects against the personnel security arrangements established by duty holders to meet Government requirements for vetting. Further information about ONR’s security team is available on ONR’s website.
We are engaging with RWM for two reasons. Firstly, to ensure that any future applications for a GDF take full account of our permitting and licensing requirements. Secondly, to ensure that the advice RWM currently provides to waste producers, about how they should package their radioactive waste for future geological disposal, is appropriate.
We maintain an open and constructive dialogue with RWM. This is beneficial in building RWM’s understanding of our regulatory expectations. It also gives us an awareness of RWM’s work in relation to geological disposal, allowing us to better plan how we will regulate a GDF in the future.
We have no regulatory role in the decision-making process for selecting potential sites for a GDF. However, separate to our oversight of RWM reported here, we also provide advice and comment on matters within our regulatory remits to inform that decision-making process.
As independent regulators, we are committed to making our work open and transparent. We trust that this report will be useful to others in introducing our standards and requirements for a GDF and in providing insight into how we will ensure that these will be met in the future. Executive Summary
Government policy for managing higher activity radioactive waste (HAW) in the long term is through geological disposal. This is currently being progressed alongside ongoing interim storage and supporting research.
published on 2 October 2017, reveals on page 11 the following information :
DISTINCTIVE is the academic programme co-funded by the EPSRC with support from industry partners from the nuclear sector. The purpose is to carry out internationally leading science and engineering research in an area of decommissioning and nuclear waste management with Sellafield Ltd providing technical supervision and direction.
Development of glass-ceramic and formulations, and hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process, for immobilization of UK plutonium stockpile, supported by hands-on Pu-239 validation at the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO).
But despite visiting the ANSTO web site, no detail of this collaborative RD&D project could be found. However, it is important, as it suggests there could be plans to immobilize plutonium in a waste form that would preclude its possible future re-use in MOX fuel. However, this would have very significant implications for the matrix of the subterranean plutonium waste packager stores in any GDF
Radioactive Waste Management Limited (RWM) is responsible for implementing government policy on geological disposal of HAW and for providing radioactive waste management solutions. It is currently undertaking preparatory work to plan for geological disposal – work described as ‘generic’, as no sites have been identified yet.
Our dialogue with RWM is helping it to develop a good understanding of the regulatory requirements and associated regulatory submissions required to enable environmental permitting and the issue of a nuclear site license.
This report summarises the work carried out by the Environment Agency and the Office for Nuclear Regulation to scrutinise the work of RWM during the financial year 2016-17. The main outcomes from our work in this reporting period are as follows:
• We have previously advised RWM that it needs to consider the chemotoxic impacts of pollutants from a GDF (in addition to the radioactive impacts), and we recently explained how we will apply the ‘prevent’ requirement of the Groundwater Daughter Directive. RWM has begun to identify hazardous substances that are most likely to challenge groundwater protection and the design measures it will need to take. We note that RWM will need more detailed information about chemotoxic substances in wastes than is currently present in the UK Radioactive Inventory.
• In preparation for our review of RWM’s 2016 generic Disposal System Safety Case next financial year, we discussed with RWM the significant changes it has made since its 2010 version, and noted its good progress with addressing our earlier recommendations. Our audit of the use of the data and models that underpin the safety case, by RWM and its contractors, has assured us that RWM has improved its systems and controls in this area. We note that gathering, managing and interpreting data is crucial to many of RWM’s areas of work (especially during the site characterisation phase).
• RWM’s Science & Technology Plan provides a good overview of the Research & Development (R&D) that RWM intends to undertake over the next decade as part of its generic work programme. It is a useful tool to help RWM explain its planned R&D and the further R&D that may be required to implement geological disposal. RWM’s Research Status Reports give a good description of the science and technology underpinning geological disposal of UK HAW and provide a useful source of reference.
The problem is RWM does not take on board technical and procedural criticisms of its unresolved research issues. The Nuclear Waste Advisory Associates (NWAA) met about twice a year with RWM (L) for several years on its unresolved issues agenda, but the meeting stopped a year ago with hundreds of unsolved issue still on the list.
Instead of listening and acting on constructive criticisms, RWM has a strong institutional tendency to be defensive, and justify its failure to address certain difficult unsolved technical problems, rather than accepting them, and trying to deal with the criticisms.
• RWM has implemented procedures and methodologies to improve its disposability assessment of packaging proposals and associated waste package records. This has given us further confidence that RWM’s disposability assessment process is providing waste producers with the waste packaging advice they require.
• We are tracking RWM’s organisational development through a series of inspections and meetings. We are satisfied that RWM is making good progress towards ensuring that it will have the right people, skills and systems in place by the time it applies for the necessary environmental permits and a nuclear site license.
page ii
Contents
1. Introduction 1
Managing our advice to RWM 1
2. Planning for implementing geological disposal 2
Groundwater (Daughter) Directive 2006 2
Optimisation 3
Safeguards 3
Lessons from international incidents 3
3. Disposal system specification and design 4
GDF design 4
Inventory 4
4. Safety case development 5
Review of RWM’s generic disposal system safety case 5
Transport safety 5
5. Research and development 6
RWM’s Science & Technology programme 6
RWM’s research status reports 6
The implications of voidage associated with ILW in a GDF 7
6. Site evaluation and characterisation 7
Sealing deep site investigation boreholes 7
Preparations for surface-based investigations and data management 7
7. Waste packaging advice & assessment 8
RWM’s process of disposability assessment 8
Waste package specifications 9
Waste package records 9
Waste acceptance criteria 9
RWM’s HAW Programme 9
8. Organisational development 10
Organisational Structure 10
HSSEQ function and quality management 10
Control and Assurance 11
ANNEX A: List of Regulatory issues and observations 12
ANNEX B: Glossary 13
REFERENCES 15 page iii
1. Introduction
Radioactive waste has arisen and continues to arise from the UK’s historic and ongoing nuclear power, research and defense programmes. To date there is no disposal route for the waste generated that is termed Higher Activity Radioactive Waste (HAW). Instead, HAW is stored on nuclear sites awaiting a disposal solution. HAW continues to be produced from nuclear sites and in smaller amounts from other users of radioactive material such as industry, hospitals and universities. New nuclear power stations, as proposed for England and Wales, would add to the amount of HAW produced.
It is important that the report admits there is currently no disposal (indeed or long term storage) route for HAW. What is unacceptable is the regulators continue to license nuclear operations that creates more radiotoxic HAW waste burden in Great Britain.
UK government policy for the long-term management of HAW is set out in the 2014 white paper [1], which sets out the framework for managing HAW in the long term through geological disposal, focusing on how a geological disposal facility (GDF) would be implemented in England.
The Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA) is responsible for implementing government policy on the long-term management of radioactive waste, and Radioactive Waste Management Limited (RWM) is responsible for implementing government policy on geological disposal of HAW.
The Environment Agency (EA) and the Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) are responsible for ensuring that any future GDF in England meets our high standards for protecting people and the environment when it is being developed, while it is operating, and after it has closed, for our respective regulatory remits of environmental protection, safety, security, radioactive materials transport and safeguards. We will be responsible for granting the necessary nuclear site license and environmental permits throughout this period. Regulatory control is likely to be required for at least a century. We are engaging with RWM now to ensure that any future applications for the development of a GDF we receive will take full account of our permitting and licensing requirements and to ensure that the advice RWM currently provides to waste producers, about how they should be packaging their radioactive waste for future geological disposal, is appropriate. This early engagement will also allow us to prepare for any license or permit application we receive from RWM, in order to respond in an informed and timely way.
We are currently preparing a paper that gives an overview of our regulatory processes that will apply in England to design assessment, construction, operation and closure of a GDF.
Managing our advice to RWM
At this early stage, before formal licensing or permitting begins, we are providing advice to RWM, as opposed to making regulatory decisions. We scrutinise RWM and provide this pre-application advice through an ongoing programme of work, the scope of which is agreed each year with RWM.
This pre-application period could span decades, so we have established systems and controls, such as the Regulatory Issue Resolution Process (RIRP) described below, to ensure that our advice throughout is auditable and that RWM’s efforts to address regulatory matters is monitored. RWM is tracking recommendations that have arisen from our scrutiny work since the early 2000s, which it uses as part of its demonstration of progress.
This really requires a fully funded stakeholder panel to oversee developments. The current stakeholder oversight of RWM is non-existent, of NDA is totally inadequate, and the EA has no stakeholder forum at all. Only ONR holds regular stakeholder forums – usually twice a year – but they are the subject of several long-standing criticisms by participants and would-be participants.
If, through our regulatory interactions, we identify an important regulatory matter, we discuss it with RWM. If the matter cannot be quickly or easily resolved through our routine dialogue with RWM, we log and monitor it through the RIRP. The process complements our routine dialogue with RWM – it does not capture all matters that we identify or discuss as a result of our regulatory interactions. Nor does it contain every important regulatory matter that a developer of a GDF will need to eventually resolve.
Matters that are considered to be important for regulatory decision-making, or the provision of regulatory advice, are graded in the RIRP as either Regulatory Issues (RIs) or Regulatory Observations (ROs). The regulators require RIs to be resolved within a specified timescale. ROs are considered to be less urgent and, for example, might require information that can only be obtained at a future stage in the programme once a site has been identified. However, ROs still require timely progression and resolution at the earliest stage possible in the programme to enable progress.
Separately, RWM records and tracks issues raised by external stakeholders that may affect the implementation of geological disposal on its own issues register. RWM’s issues register includes some of our regulatory issues and observations for completeness, and contains many more issues from a much wider audience. RWM has published and updates its issues register on its website and we consider this to be a significant step towards transparent decision-making.
2. Planning for implementing geological disposal
We are engaging with RWM to ensure that any future applications for the development of a geological disposal facility (GDF) will be right first time and take full account of our permitting and licensing requirements.
This sounds like a positive aspiration, except there is no way any external stakeholder can judge whether RWM get it “right” – first time or otherwise!
This will help to avoid unnecessary delays that might result if RWM were to provide inappropriate or incomplete information in support of any license or permit application.
Groundwater (Daughter) Directive 2006
The Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC) and the Groundwater Daughter Directive (GWDD, 2006/118/EC) require EU Member States to protect groundwater against pollution and deterioration by preventing or limiting entry of pollutants to groundwater. Certain provisions of the Directives have been given effect in England and Wales through Environmental Permitting (England and Wales) Regulations 2016 (commonly referred to as EPR 2016).
The GWDD states that in order to achieve the objective of preventing or limiting inputs of pollutants into groundwater, ’necessary and reasonable’ measures should be taken to prevent inputs into groundwater of any hazardous substances, with the input of non-hazardous substances limited in such a way as to ensure that such inputs do not cause deterioration or significant and sustained upward trends in the concentrations of pollutants in groundwater. Generic guidance is available [2, 3]. However, there is no specific guidance as to how the ‘prevent’ requirement should be implemented in the context of a GDF.
We recognise that it is not possible to contain hazardous substances absolutely and indefinitely in any facility, particularly over the timescales that a GDF will operate. This is recognised in paragraph 4.31 of UK Groundwater Activities Guidance [4], which states ‘For disposals of any solid wastes, absolute and indefinite containment of pollutants within a disposal facility will not be achievable… these facilities should be designed such that the long term inputs of hazardous substances to groundwater will be insignificant from an environmental and human health perspective’.
In our advice to RWM [5] we explained how we will interpret the ‘prevent’ requirement and how we will expect the operator of a GDF to take all necessary and reasonable measures to avoid the entry of hazardous materials associated with radioactive wastes into groundwater and to incorporate these measures into the design of the GDF.
RWM has begun identifying hazardous substances likely to challenge groundwater protection requirements, and is currently reviewing an initial selection of 20 hazardous substances [6]. We assessed RWM’s progress towards being able to determine how hazardous substances, associated with radioactive materials in a GDF, may impact on post-
2
closure safety and protection of people and the environment [7]. We recognise that RWM’s work in this area is at the early stage of a longer programme of work, as set out in its Science &Technology (S&T) Plan [8], and that inventory data is relatively sparse. In this context, we consider RWM’s work to date is appropriate as a basic exploration of the issues. We will continue to monitor RWM’s ongoing work in this area (GDF_RO_ 001 – see Annex A).
Optimisation
RWM will need to demonstrate that a GDF is optimised for radiological protection. Previously, we identified a misunderstanding of aspects of this requirement (recommendation 55 of [9]).We have been formally tracking our ongoing dialogue with RWM to achieve a common understanding via a RO (GDF_RO_ 002 – see Annex A).
From RWM’s response [10] to the RO we consider there is still potential for confusion in RWM’s definition of optimisation and optioneering. We have advised RWM to support resolution of this matter and will consider whether its subsequent response adequately addresses the potential for confusion.
Safeguards
We have previously engaged with RWM to provide advice on the application of safeguards at a GDF. RWM reflected ONR’s advice in its paper to EURATOM [11].
Despite this 50 page paper, it does not explain how any waste packages subject to safeguards (eg containing fissile material) will be stored above ground if technical problems in any GDF require the complete retrieval of the inventory; and how these re-positioned waste packages would be safeguarded and secured under the new storage arrangements.
ONR met with RWM in February 2017 to provide an update on Safeguards implications from the UK’s decision to leave the European Union and the Euratom Treaty. Both ONR and RWM agreed to continue working to current arrangements until the exact implications for Safeguards in the UK, and hence at a future GDF, have been determined.
Lessons from international incidents
We asked RWM to consider lessons learnt from two recent nuclear incidents. We are tracking these requests through two Regulatory Observations (GDF_RO_ 003 and GDF_RO_005 – see Annex A).
In our review of RWM’s generic Disposal System Safety Case (gDSSC) in 2011, we asked [9] RWM to consider the lessons learnt from the Fukushima disaster in the context of its geological disposal programme. RWM identified three areas that it needs to include in its illustrative designs for the GDF and the design and safety assessment process: loss of power, mitigation of loss of containment, and provision of mobile equipment. In addition, RWM has considered the credibility of faults and the requirement for mitigation against the generic design basis, and has considered the recommendations and requirements for non-nuclear power plants thoroughly and applied them to the GDF. We are satisfied that RWM has taken on board lessons from the Fukushima disaster and we consider the matter resolved [12].
This summary makes no mention of the likely requirement post an accident involving the airborne dispersal of radioactivity of radioactive remediation on a large scale and the subsequent need for very long term storage of the radioactively contaminated soil and biota after containment. It should have.
Following the two incidents at the US Department of Energy Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) in New Mexico in 2014, we asked RWM to review the implications for a GDF and the organisation implementing and operating it. RWM has prepared a response to our RO (GDF_RO_005 – see Annex A), and is updating it to include lessons from discussion with the Chair of the Accident Investigation Board into events at WIPP and advice from its Nuclear Safety and Environment Committee (NSEC). We will consider whether RWM has addressed our concerns once we receive its response to the RO. 3
3. Disposal system specification and design
RWM will need to demonstrate to us that its geological disposal system provides the necessary protection for people and the environment. We expect RWM to show how, at the early design stage, that it is taking into account our requirements. This includes how the facility and its structures, systems and components are identified and selected to achieve an optimised design.
GDF design
RWM included a Design Status Report on the list of 2016 generic Disposal System Safety Case (gDSSC) deliverables under the heading ‘supporting references and associated documents’. As such it is not part of the safety case, but it documents design decisions. We will consider whether we need to look at the Design Status Report in detail when we review the 2016 gDSSC.
RWM will need to maintain its scientific capability for reviewing and reporting on developments with respect to alternative management options, including deep borehole disposal. We attended the 1st International Meeting on Deep Borehole Disposal of HLW in June 2016 that was also attended by RWM and the Committee on Radioactive Waste Management (CoRWM). We are pleased to note that RWM is maintaining a watching brief of international developments and is actively engaging with other (international) organisations. We note that deep borehole disposal is under investigation in other countries as an alternative or complementary management approach for certain waste types and, at the least, there could be possibilities for cross-learning.
Inventory
The NDA worked with Department for Energy and Climate Change (DECC, now BEIS) to deliver the 2013 United Kingdom Radioactive Waste Inventory (UKRWI), which provides the basis for RWM’s ‘Inventory for geological disposal’ for the 2016 gDSSC. We will consider the suitability of RWM’s inventory for geological disposal in our review of the 2016 gDSSC.
RWM will need more detailed information about the chemotoxic substances present in the waste destined for a GDF than is currently included in the UKRWI: In particular for substances that are classified as hazardous substances or non-hazardous pollutants under the terms of the GWDD. This information is vital to enable RWM to assess the impact of non-radioactive substances against the requirements of the GWDD. RWM must continue to engage with the NDA, its contractors and waste producers to ensure that future iterations of the UKRWI (2019 onwards) meet RWM’s needs with respect to the inventory of hazardous substances and non-hazardous pollutants in waste destined for geological disposal. This matter is subject of wider ongoing engagement with RWM (see discussion at 2.1).
From our work with the NDA and the wider nuclear industry, it is clear that better waste characterisation and assaying techniques offer the potential for some intermediate level radioactive waste (ILW) to be reclassified to low level waste (LLW). We asked RWM how robust its work is, should significant reductions in the ILW inventory occur.
It is a clear concern that by reclassification of radioactive waste stream, thereby creating a bigger burden on LLW which requires a lesser level of – and probably cheaper – protective packaging, this would reduce public and environmental protection. This reclassification should be denied by regulators if driven by cost reduction pressures.
It is also essential to know what proportion, if any, of the current stockpile of fissile material especially plutonium and highly enriched uranium (HEU) that is to be classified as a waste, and is therefore destined for emplacement in any GDF.
RWM explained that such changes would be promulgated through the UKRWI which would, in due course, be factored into its inventory for geological disposal. RWM also noted that its uncertainty scenarios for the inventory in the 2016 gDSSC provide some resilience for such circumstances.
i Previously referred to as the ‘Derived Inventory’ 4
4. Safety case development
An application relating to a proposed disposal of solid radioactive waste must be supported by a suitable environmental safety case.
Any such safety case must involve the safety and security aspects of transport from one or more storage sites – following conditioning and packaging of the waste streams- to the one or GDFs developed. This would also apply if an above ground final store were opted for instead of a GDF
Similarly, any application for a nuclear site license to construct and operate a GDF will need to be supported by adequate demonstrations of safety and security [13]. A safety case should contain the collection of the claims, arguments and evidence that support the safety of a facility. Development of a safety case for a GDF is complex. It is recognised internationally that continual dialogue between the regulators and the developer, from the very early design stage, is essential.
We want RWM to understand clearly what we require it to demonstrate, and when, through its environmental, operational and transport safety cases.
Review of RWM’s generic disposal system safety case
We held a series of discussions with RWM to understand the aims and objectives of its 2016 gDSSC and to help us plan our review of it. RWM also provided us with an update on its progress in addressing the recommendations from our review of its 2010 gDSSC and briefed us on the most significant changes to the gDSSC. These include: adoption of the 2013 derived inventory; modifications to reflect the 2014 white paper [1]; new container designs for Low Heat Generating Waste (LHGW) & legacy High Heat Generating Waste (HHGW); and evidence on how waste disposal operations could be safely carried out in a range of geological environments. RWM also informed us of those parts of the gDSSC it considers will be transferable to a site specific DSSC [14]. We will review the gDSSC in 2017 and publish a report on our findings and recommendations in 2018.
We inspected RWM’s (and its contractors’) use of data and models, as applied to the 2016 gDSSC [15] and concluded that RWM has improved its procedures for data management and model development since our previous inspection in 2014. We recognise that it has taken significant effort to implement the current system, which we consider now ensures good traceability of data and controlled use of data and models. RWM staff and contractors were very knowledgeable in their areas of expertise. They demonstrated in-depth awareness of the data management and modelling procedures and understood the importance of implementing them correctly. We identified many examples of good practice during our inspection and identified a number of areas where we consider RWM could further improve its management of data and models.
Transport safety
ONR, as the UK transport competent authority, was invited by RWM in March 2017 to provide early feedback on the current design proposals regarding the development of a disposal container and associated transport container for high level waste and spent nuclear fuel from pressurised water reactors and advanced gas-cooled reactors (should these be declared waste in the future).
The proposed design incorporates a multi water barrier concept. This is similar to a Russian doll arrangement where the disposal container body and welded lid is the inner water barrier and the transport container body and lid is the outer water barrier. The concept of a multi water barrier has never been approved in the UK. However, there are examples internationally.
ONR has considered RWM’s proposals and will provide a response to RWM in 2017/18. 5
Realistic accident and terrorist attack scenarios, along with with projected radioactive dispersal outcomes, need to be modelled in the context of the inevitably increased vulnerability of radioactive waste/spent nuclear fuel (SNF) transported on public railways and road. It is certainly not sufficient to refer to secret Design Basis Threat (DBT) assessments: the public who could be as affected for decades by an accident tor incident need to know both the hazards (problematic dangers) and risks (likelihood).
5. Research and development
We want to be assured that the best scientific knowledge and engineering practice will underpin any future GDF. We expect RWM to undertake a comprehensive research and development (R&D) programme, informed by wider national and international research or implementation programmes. RWM will need to identify and address, in a timely manner, the issues that require R&D to meet our requirements. This will help RWM to avoid unnecessary delays when requesting regulatory approval for the various stages of geological disposal and it will reduce the likelihood of us needing to specify R&D actions mid-way through any licensing or permitting process.
This is the correct approach, but RWM in public and to politicians and ministers continue to insist the main safety issues are resolved, while it is known – mainly from the engagement work with RWM done by NWAA across several years – that around 1000 unresolved safety issues remain. More public honesty and political transparency is needed by RWM on this: they seem more determined to give reassurance to politicians they can deliver their mission than be honest about its enduring difficulty.
RWM’s Science & Technology programme
We reviewed RWM’s updated Science and Technology (S&T) Plan [16], in particular focusing on how RWM has addressed our comments on its previous version [17, 18] and how RWM manages changes to its research programme. The document provides a good overview of the R&D that RWM plans to undertake over the next decade as part of its generic work programme. We consider that it provides RWM with a good tool to use as a basis for engaging with others, to explain the R&D it plans to undertake and also the further R&D that may be required to implement geological disposal. The document will help RWM’s preparations for any future site-specific programme of work. The document provides a good explanation of how RWM plans to use scientific readiness levels (SRLs) to demonstrate how it is addressing its knowledge gaps, and a useful summary of the drivers that RWM has used to establish a focussed R&D programme. We commend RWM on its national and international collaboration on R&D to date, but note the large amount of novel work that is likely to be required as the GDF programme progresses.
ONR engaged with RWM specifically on research relating to operational safety at a GDF, to identify if RWM’s research plans in this area are consistent with ONR’s expectations, taking account of the current stage of GDF development. ONR’s regulatory research register [19] project on this topic identified the following recommendations for RWM to consider regarding its R&D programme [20]:
• RWM should develop its arrangements to include a clear process that ensures that the identification of research needs is integrated into the design process.
• RWM should include the requirement to develop its arrangements for the identification of research needs at the various stages of the GDF development into its forward plan.
• RWM should develop its arrangements to ensure that the process of technology transfer includes an assessment to identify any research needs.
This is an appropriate insistence, which RWM consistently plays down, because it does not want to scare ministers how far they are from resolving unsolved (perhaps unsolvable) technical safety issues. The comments on dealing with RWM ‘information gaps’ below goes part way to addressing this problem
RWM plans to address these recommendations during 2017/18 as part of the development of its Technical Programme.
RWM’s research status reports
We reviewed RWM’s research status reports [21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29], as stand-alone documents, not as part of any safety case submission. We consider that they fulfil their stated purpose to describe the science and technology underpinning geological disposal of UK higher activity waste, by providing a structured review and summary of relevant published scientific literature and discussing its relevance in the UK context. They provide a useful source of references that would allow someone with a broad knowledge of geological disposal to understand the subject. The status reports do not (and were not intended to) highlight safety arguments obtained from the underpinning knowledge base, nor do they identify knowledge gaps. We are not concerned that RWM has separated its evidence base from safety arguments, provided we are able to trace the safety arguments back to underpinning evidence when we assess the 2016 gDSSC and any future generic or site-specific safety cases.
6
We advised RWM how it could improve the status reports when it next updates them, including how it should develop the cross-referencing between the status reports and individual tasks in the S&T Plan in future iterations. This should help the reader understand the information gaps, their significance, and RWM’s plans to investigate them.
The implications of voidage associated with ILW in a GDF
We need to understand RWM’s approach to challenges posed by the potential disposal of non-encapsulated waste at a GDF; the issues that it is considering, and how it is addressing them.
We consider that RWM has made good progress, recognising that its work so far in this area [30, 31, 32] represents the start of a longer research task. RWM’s current level of understanding is appropriate, given the current generic stage of the UK programme, and should help RWM implement any necessary changes to its packaging advice in a timely manner. We will continue to engage with RWM on this matter and to monitor RWM’s progress towards developing a broader and more comprehensive understanding of the nature and significance of voidage on disposability and GDF performance.
6. Site evaluation and characterisation
RWM will need appropriate plans and procedures in place to undertake the wide range of site evaluation and characterisation activities required to implement geological disposal. We want to ensure that RWM’s plans and actions for future investigations are consistent with the EA’s permit requirements for intrusive site investigations.
Sealing deep site investigation boreholes
RWM will need to satisfy us that its plans for sealing deep investigation boreholes are suitable, before we allow it to start drilling the boreholes.
At a workshop on the sealing of deep site investigation boreholes [33], we informed participants of the recently updated and published list of hazardous substances and minimum reporting values [34], and we advised RWM of a number of matters to consider as it progresses work in this area, including the need to:
• protect groundwater resources, particularly if considering using chemicals in the sealing process
• demonstrate the ability to seal any boreholes before applying for a drilling permit
• update the demonstration of how sealing will be achieved if plans change during or after drilling (for example, if a new decision is made to use investigation boreholes for long-term monitoring).
Preparations for surface-based investigations and data management
RWM will need to demonstrate to us that its plans for gathering, interpreting and managing the data required as part of its site investigation programme are suitable, before we allow site investigation to start.
RWM provided us with an update of its plans and progress towards developing systems and procedures to collect and manage data from site investigation. RWM is developing a site characterisation programme for 4 scenarios that cover different rock types and timescales. Through sensitivity analysis, RWM has found that the site characterisation programme is influenced more by the number of boreholes required rather than the rock type. Critical path activities are borehole drilling and informing the Development Consent Order (DCO). 7
We agree with RWM that development of a data management system (DMS) is an essential component of its site investigation programme for managing scientific data and making the right data available to all users. RWM’s work on the DMS stopped in 2013, but it is now developing a future work programme and reviewing its DMS procurement activities. We note that developing the DMS could become on the critical path and RWM should progress this in a timely manner so that it does not have the potential to prevent or delay regulatory decision-making relating to borehole investigations.
This is a crucial area where public distrust is rightly high. The MWRS programme pursued by RWMD was essentially halted because Cumbria CC refused to believe that if permission were to go ahead to this borehole drilling phase, it would not inexorably lead to the site being characterized also being chosen, even if found to be unsuitable. This concern remains.
7. Waste packaging advice & assessment
RWM provides advice to waste producers on the packaging of their HAW. It has developed a process of disposability assessment to minimise the risk to waste producers that waste packaged now will be unsuitable for disposal in a GDF in the future. This packaging advice is used by waste producers to inform their safety cases and can be included as part of a radioactive waste management case.
RWM’s process of disposability assessment
Our inspection in 2013 has given us confidence that RWM’s disposability assessment process provides waste producers with the information and advice necessary to minimise the risks that HAW stored on licensed sites will not be suitable for safe handling, transport, storage and disposal in the future. RWM has developed the structure of its waste team, with the creation of additional senior posts and packaging assessment resource, although some further work remains to be done to this. RWM informed us of how its existing disposability assessment methodology can be flexed to consider differences or extensions from an existing endorsement, or based on precedent, aiming at a more flexible and proportionate approach.
The regulators need to know how they would handle waste from accidents within nuclear cores i.e. dealing with distorted, broken or otherwise dangerous SNF due to in-core accidents, such as have happened in the past at Dounreay; also regulators need to know from RWM and nuclear operators how they would condition and package waste from nuclear accidents involving on-site & off site dispersal of radioactivity and hence soil and biota waste streams arising, all the detail addressed in the above commentary seems to concentrate on radioactive waste arising from normal operation of nuclear power plants and reprocessing plants. Abnormal operation and accidents, as well as damaged so-called ‘exotic’ SNF imported from research reactors and presently stored at Dounreay, also need urgent attention.
We have been monitoring RWM’s progress, via a number of Regulatory Issues.
• GDF_RI_006 (Resolution of Periodic Review Findings): RWM has introduced a Periodic Review procedure and supporting work instructions, which control the re-endorsement of a packaging process/packages at the time of a Periodic Review. We are satisfied that RWM now has adequate measures in place and we consider the matter is resolved [35].
• GDF_RI_007 (Assurance of packaging assessments and advice): we are satisfied that RWM has made adequate progress with respect to improving its internal assurance and independent oversight functions and we consider these issues are now resolved [35].
• GDF_RI_011 (Waste package records): we wanted assurance of RWM’s continued efforts to work with waste producers to ensure that appropriate information is identified, collected and maintained as part of a waste package record to demonstrate disposability and to support the long term management and final disposal of wastes. RWM implemented a package records project in 2015 involving regular dialogue with NDA, waste producers and regulators, and has published revised guidance (section 7.3). Through this engagement we are satisfied that RWM is working closely with industry to ensure waste package records will meet the required standard and we consider the issue is now resolved [35].
• GDF_RI_005 (Assessment of Innovative Packaging) and GDF_RI_010 (Sensitive disposability assessments and endorsements): remain open as RWM has work ongoing to address our comments [35].
In 2010, ONR and the Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA) concluded that RWM’s disposability assessment process provides suitable advice to support the long-term management of HAW in near-surface facilities, in accordance with Scottish HAW policy. In 2016, ONR together with SEPA, considered it timely to review that position. The EA provided support to ensure continuity with the similar inspection it and ONR undertook in 2013 that considered the application of the HAW disposability assessment process in England and Wales [36]. At the time of writing, a report detailing the inspection findings and conclusions was being finalised and will be published in 2017/18. 8
Waste package specifications
Following our review of a suite of RWM’s Generic Specifications for LHGW, Depleted, Natural and Low Enriched Uranium (DNLEU) and HHGW [37, 38, 39], we advised RWM [40] to:
• use an appropriate level of change control to maintain its packaging specifications.
• clarify in its key documentation the relationship between, and the procedures linking, the development of generic packaging specifications, disposal facility designs, and safety cases.
• clarify why it has not addressed spent fuel arising from future nuclear power stations in the generic specification for HHGW.
It is surprising that the regulators state RWM has not specified how it plans to package this high heat generating waste, but does not explain what has been done to rectify this anomaly.
Reference 41(ie Waste Package Records Approval Preferred Option Paper. NSG Environmental Ltd, Ref Report NS3640/500/003, issue 1, September 2016) is not available on the NSG Environmental Ltd to assess.
Such reference should be easily publicly available if readers of this annual report are invited to offer review comment!
• clarify how the generic specifications for DNLEU and HHGW can be used to assess, and potentially endorse, packaging proposals or wastes already conditioned.
Waste package records
RWM’s contractor report [41] sets out the preferred option for the approvals process for waste package records. In particular, we advised RWM that the process should demonstrate the essential links with the disposability assessment and letter of compliance (LoC) process, through which the quality of records are assessed and agreed.
Waste acceptance criteria
We advised RWM of a number of areas where it should clarify its intent with respect to its approach to developing waste acceptance criteria (WAC) for a GDF [42, 43], including:
• How RWM’s proposals for the development of WAC link to the stages in the implementation of geological disposal (including any differences in timescales for the development for different categories of waste)
• RWM’s justification for its preferred approach to develop WAC, the implications of this for waste producers, and any other methodologies it has considered
• The comprehensiveness of RWM’s engagement with other relevant waste management organisations and with operators of facilities used to store and export HAW and spent fuel, to inform its development of WAC.
We will continue this dialogue with RWM through our ongoing pre-application advice and scrutiny programme.
RWM’s HAW Programme
RWM’s HAW Programme is a new programme that includes taking forward opportunities from NDA’s previous Upstream Optioneering programme as well as new areas of work, such as the Problematic Waste and Near Surface Disposal Integrated Project Teams (IPTs). We engaged with RWM to improve our understanding of the aims, objectives, activities and timescales of its HAW Programme and to determine our strategy for scrutinising this work. We advised RWM that given this is a national strategic activity, RWM should continue its efforts to incorporate non-NDA sites into its work programme. We also highlighted the need for RWM to consider how best to demonstrate and present an integrated picture of work associated with HAW. We will continue to engage with RWM in this area. 9
Interested parties need to know what proportion of the already reprocessed plutonium stockpile will be incorporated into the HAW inventory.
8. Organisational development
RWM must establish and develop its structure and management arrangements appropriate to an organisation capable of holding the necessary licences and environmental permits to develop and operate a GDF. We monitor RWM’s progress as a prospective Site Licence Company (SLC) through a series of inspections and meetings that have resulted in a number of Regulatory Issues. The following is a summary of RWM’s progress towards addressing these matters.
Organisational Structure
In April 2015 RWM adopted a new organisational structure to support implementation of geological disposal, and its wider remit of HAW management, including new roles (e.g. GDF Siting Director, Head of HAW programme), and 23 new posts. RWM has progressively reduced the number of interim staff in important safety roles by continuing to recruit permanent staff into these roles. Whilst RWM continues to employ interim staff in important posts, we are pleased to note that it treats these individuals in the same manner as permanent staff.
In its organisational baseline document RWM identified vulnerabilities in its resources and has implemented a competency framework, which it plans to apply to baseline competencies at all levels of the organisation. We are satisfied with RWM’s progress in this area and we consider the associated Regulatory Issue (GDF_RI_002 Organisational Capability) is resolved. We also consider the integration of Quality into RWM’s Health, Safety, Security, Environment, and Quality Department, in 2015, resolved the first part of GDF_RI_009 which required RWM to “ensure an appropriately resourced, well directed and integrated internal assurance function”.
RWM’s Organisational Baseline Document (OBD) and the associated procedure [44, 45] provide an important element in demonstrating that the company has the organisational structure, staffing and competences expected at this stage of its development and that it has considered the risks associated with organisational changes. We advised RWM to focus on three main elements of the OBD: organisation, resources and competences; using indicators at the department level (rather than across the company) to identify vulnerabilities and potential conflicts in posts; and implementing more specific succession planning deeper into the organisation.
It is unclear what “conflicts in post” means; this should be spelled out clearly
We also advised RWM to implement its Management of Organisational Change procedure across the company.
HSSEQ function and quality management
RWM has appointed a special adviser on Health, Safety, Security, Environment and Quality (HSSEQ) matters and its HSSEQ function now advises the RWM Board on key performance indicators relevant to safety and environmental performance. RWM has continued to review the role, remit and need for its various groups and committees and has reduced the number of these, ensuring throughout that all staff are clear on the purpose and remit of each.
We note that there is a continuing but reducing disparity across the organisation in understanding the main hazard areas that RWM is responsible for managing, for example, HAW packaging, GDF siting, safety case production, staff retention, and information security. However, overall, we are satisfied with RWM’s progress in this area and we consider the associated Regulatory Issue (GDF_RI_001 Leadership & Governance) is resolved.
RWM has appointed a Head of Organisational Learning and Development within the HSSEQ function. It has reviewed its organisational learning process, and benchmarked itself against other organisations. RWM is implementing new formal organisational learning and improvement arrangements, and has completed a Data and Models Compliance Project, which we have inspected [15]. RWM collaborates with, and participates in, a number of external groups and obtains operating experience from several external sources.
It would be helpful for external interested parties invited to comment who these “external groups and sources” are: detail should be provided.
RWM has implemented changes from its learning from incidents at Fukushima and WIPP (as discussed earlier), and the rock fall at the underground laboratory at Bure.
Details of the relevance of the Bure incident at France’s ‘flagship’ subterranean radwaste disposal site needs to be spelled out.
It has made substantial progress in implementing its organisational arrangements and we consider the Regulatory Issue is resolved (GDF_RI_004 Organisational learning).
RWM has summarised the responsibilities of its Board and HSSEQ sub-committee with regards to the quality management system and management system auditing (in its written response to GDF_RI_008 Board governance of important areas of risk/performance), which together with the supporting documentation [46, 47, 48, 49], and combined with the findings of our inspection in February 2016 [50], demonstrate significant improvements in this area, such that we consider the RI resolved.
Control and Assurance
RWM has acknowledged that it will need to act as an intelligent client with major contractors during the implementation of geological disposal and is including this in its development of competences within RWM. We asked RWM (GDF_RI_009) to review its current programme of audits of its supply chain and to ensure that its programme is consistent with RWM’s stated role as a thin client. RWM has discussed its supply chain audits internally (via its Commercial Working Group), which prompted it to take a wider look at supplier evaluation. RWM has not yet given us an update on what this means for supply chain audits, therefore the matter (and the RI) remains unresolved pending a suitable response from RWM.
From the point of view of external interested parties, the most important aspect is these audits need to be open and transparent. All too often, these arrangements are covered by alleged and unacceptable ‘commercial confidentiality.”
We advised RWM (GDF_RI_003 Control & Assurance) to:
• review its arrangements for assurance to ensure that they are robust and consider nuclear as well as conventional issues of safety and environment performance
• review and develop its safety and environment management system to ensure the proper control and assurance of nuclear safety and environment issues
• develop an autonomous management system with an effective assurance and review processes, to ensure that reference to, and control of, the safety case is fully integrated into business management processes.
RWM has made progress in developing its management systems to support its work, and has achieved ISO19001 and ISO14001 accreditation. We consider that control and assurance are now part of normal business for RWM and the Regulatory Issue (GDF_RI_003) is resolved.
As a general final comment, the fact there is zero reference to stakeholder involvement or engagement demonstrates the limited attention the regulators have given and do give to stakeholder input, especially from NGOs and their nominated independent experts. This needs to be rectified, both to make the disposal/long term storage proposal better, and more transparent to external interested parties.
ANNEX A: List of Regulatory issues and observations
Current Regulatory Issues and Regulatory Observations:
RI Number
Title
Status
GDF_RI_001
Leadership & governance
Closed
GDF_RI_002
Organisational capability
Closed
GDF_RI_003
Control & assurance
Closed
GDF_RI_004
Organisational learning
Closed
GDF_RI_005
Assessment of innovative packaging proposals
Open
GDF_RI_006
Resolution of Periodic Review Findings
Closed
GDF_RI_007
Assurance of packaging assessments and advice
Closed
GDF_RI_008
Board governance of important areas of risk/performance
Closed
GDF_RI_009
Corporate HSSEQ structure
Open
GDF_RI_010
Disposability Assessments and Endorsements sensitive to changes
Open
GDF_RI_011
Waste Package Records
Closed
RO Number
Title
Status
GDF_RO_001
Protection against non-radiological hazards
Open
GDF_RO_002
Optimisation
Open
GDF_RO_003
Lessons from the Fukushima disaster
Closed
GDF_RO_004
Defining waste package fissile limits for disposal
Open
GDF_RO_005
Lessons from the WIPP Incident
Open
ANNEX B: Glossary
BEIS Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy
CoRWM Committee on Radioactive Waste Management
DCO Development Consent Order
DECC Department of Energy and Climate Change
DMS Data Management System
DNLEU Depleted, Natural and Low Enriched Uranium
DSSC Disposal System Safety Case
EA Environment Agency
EPR 2016 Environmental Permitting (England and Wales) Regulations 2016
Euratom The European Atomic Energy Communityii
GDF Geological Disposal Facility
gDSSC generic Disposal System Safety Case
GRA Guidance on Requirements for Authorisation
GWDD Ground Water Daughter Directive
HAW Higher activity radioactive waste
HHGW High Heat Generating Waste
HSSEQ Health, safety, security, safeguards, environment and quality
ILW Intermediate Level radioactive Waste
IPT Integrated Project Team
LHGW Low Heat Generating Waste
LoC Letter of Compliance
NDA Nuclear Decommissioning Authority
NIEA Northern Ireland Environment Agency
NRW Natural Resources Wales
NSEC Nuclear Safety and Environment Committee
OBD Organisation Baseline Document
ONR Office for Nuclear Regulation
R&D Research and Development
RIRP Regulatory Issue Resolution Process
RI Regulatory Issue
RO Regulatory Observation
RWM Radioactive Waste Management Limited (from 1 April 2014)
SAP Safety Assessment Principle
ii Co-ordination of European Community activities (such as research, safety standards) for the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
13
SEPA Scottish Environment Protection Agency
SLC Site Licence Company
SRL Scientific Readiness Level
S&T Science and Technology
UKRWI United Kingdom Radioactive Waste Inventory
WAC Waste Acceptance Criteria
WIPP Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (in New Mexico, USA)
14
REFERENCES
1. Department of Energy & Climate Change. Implementing Geological disposal. A Framework for the long-term management of higher activity radioactive waste. July 2014. URN 14D/235.
2. Environment Agency (2013). Groundwater protection: Principles and practice (GP3). LIT 7660. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/groundwater-protection-principles-and-practice-gp3
3. European Commission (2007). Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive. Technical Report-2007-012.
4. DEFRA (2010). Environmental Permitting Guidance – Groundwater Activities. Version 1.0. https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/69474/pb13555-ep-groundwater-activities-101221.pdf
5. Environment Agency letter to RWM. T&O Task 1: Clarification of the Groundwater Daughter Directive ‘Prevent’ Requirement – as applied to a geological disposal facility. EA Ref OTH-16-051 dated 21/12/16
6. Post-closure study of hazardous substances in a GDF. Amec Foster Wheeler report to RWM. Ref RWM/004/087 dated 12 February 2016.
7. Environment Agency letter to RWM. Task 1: Post-closure study of hazardous substances in a GDF EA Ref GDF/PAA/2017/04 dated 25/1/2017.
8. Radioactive Waste Management. Geological Disposal Science and Technology Plan. March 2016. NDA Report no. NDA/RWM/121.
9. Office for Nuclear Regulation and Environment Agency. Joint regulatory scrutiny of RWMD’s work relating to geological disposal of higher activity radioactive waste: Regulatory review of the generic disposal system safety case. Issue 1 December 2011. GENW1211BVDX-E-E.
10. RWM Response to regulatory observation GDF/RO/002: Optimisation (of radiological protection). Technical Note Document Number (Live Link Number): 20394170. Revision 2 Dated 10th September 2015.
11. The Application of Nuclear Safeguards to a Geological Disposal Facility. RWM report NDA/RWM/133 rev 3 dated January 2016, document number 22915609.
12. Office for Nuclear Regulation and Environment Agency letter to RWM. T&O Scrutiny Task 1: GDF_RO_003 Regulatory Observation: Lessons from the Fukushima disaster with respect to the assessment of external hazards for UK nuclear facilities. Ref GDF/T&O/2016/10 dated 30 Sep 2016.
13. Office for Nuclear Regulation. Licensing Nuclear Installations. 4th Edition. January 2015. http://www.onr.org.uk/licensing-nuclear-installations.pdf
14. RWM letter to the Environment Agency and Office for Nuclear Regulation. Task 3: Aspects of the generic DSSC that may be transferable to a site specific DSSC. RWM ref LL 25487942 dated 9 Sep 2016.
15. Environment Agency and Office for Nuclear Regulation letter to RWM. Safety case development: Audit of data and models used in the 2016 gDSSC. Ref GDF/PAA/2017/01 dated 24 Jan 2017.
16. Environment Agency letter to RWM. Environment Agency Feedback on Issue 2 of the Science and Technology Plan. Ref GDF/T&O/2016/13, dated 15 December 2016.
17. Geological Disposal: Science and technology Plan. NDA Report No NDA/RWM/121. September 2014.
18. Environment Agency letter to RWM. GDF/T&O/2015/01 Review of the Science and Technology Plan. Dated 18 March 2015.
19. ONR Regulatory Research Register. http://www.onr.org.uk/research/regulatory-research-register.htm 15
20. ONR Report: Review of Progress on Research Topic ‘Safety Implications of the Design, Construction and Operation of a Geological Disposal Facility’ – March 2017.
21. Environment Agency letter to RWM. Task 5: Environment Agency Feedback on RWM’s 2016 Research Status Reports. Ref GDF/PAA/2017/02, dated 24 January 2017.
22. RWM Report. Geological Disposal. Behaviour of Radionuclides and Non-radiological Species in Groundwater. NDA/RWMD/465/01 Rev v3.0 dated 16 March 2016.
23. RWM Report. Geological Disposal. Biosphere. DSSC/454/01 Rev v3.0 dated 16 February 2016.
24. RWM Report. Geological Disposal. Criticality Safety Status Report. DSSC/458/01 Rev v3.0 dated 21 March 2016.
25. RWM Report. Geological Disposal. Engineered Barrier System Status Report. DSSC/452/01 Rev v3.0 dated 21 March 2016.
26. RWM Report. Geological Disposal. Gas Status Report. DSSC/455/01 Rev v3.0 dated 17 March 2016.
27. RWM Report. Geological Disposal. Geosphere Status Report. DSSC/453/01 Rev v3.0 dated 17 March 2016.
28. RWM Report. Geological Disposal. Waste Package Accident Performance Status Report. DSSC/457/01 Rev 3.0 dated 10 March 2016.
29. RWM Report. Geological Disposal. Waste Package Evolution Status Report. DSSC/451/01 Rev 3.0 dated 17 March 2016.
30. ASSIST report for RWMD. An initial evaluation of the nature and amount of voidage associated with an ILW GDF. ASSIST-1547B-R1 v1.0. December 2012.
31. Implications of voidage for post-closure safety of a GDF. Quintessa report for RWM. Ref QRS-1698A-1 v 2.2 Dated May 2016.
32. Managing voidage in a GDF. Ref: Quintessa report for RWM. QRS-1698E-P1 Dated 29 June 2016.
33. Amec Foster Wheeler. RWM/03/046. Sealing deep site investigation boreholes. Note from workshop.
34. Defra guidance. Hazardous substances in groundwater: minimum reporting values. Updated 13 January 2017. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/values-for-groundwater-risk-assessments/hazardous-substances-to-groundwater-minimum-reporting-values#minimum-reporting-values
35. Environment Agency and Office for Nuclear Regulation Letter to RWM dated 30 January 2017 Assessment of RWM’s responses to GDF_RI_005; GDF_RI_006; GDF_RI_007; GDF_RI_010; and GDF_RI_011. Ref GDF/PAA/2017/05 and ONR Ref RWML70024, dated 30 January 2017.
36. Inspection of RWMDs provision of disposability assessment and waste packaging advice. Environment Agency and Office for Nuclear Regulation Report, Issue 1.0, November 2013. Cat Code: LIT 8902 https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/suitability-of-radioactive-waste-disposal-assessment-and-packaging-advice
37. Geological Disposal: Generic specification for waste packages containing low heat generating waste. NDA/RWMD/068. August 2012.
38. Geological Disposal: Generic Specification for waste packages containing depleted, natural and low enriched uranium. WPSGD WPS/230/01. December 2015.
39. Geological Disposal: Generic specification for waste packages containing high heat generating waste. WPSGD WPS/240/01. February 2016.
40. Environment Agency and Office for Nuclear Regulation letter to RWM. Task 7: Review of Generic Specifications for waste packages. Ref GDF/T&O/2016/011 dated 12 August 2016. 16
41. Waste Package Records Approval Preferred Option Paper. NSG Environmental Ltd, Ref Report NS3640/500/003, issue 1, September 2016.
42. Environment Agency letter to RWM dated 15 March 2017. The Development of Waste Acceptance Criteria for a UK Geological Disposal Facility. EA reference GDF/PAA/2017/09.
43. Geological Disposal: The development of waste acceptance criteria for a UK geological disposal facility. RWM Technical Note no. 24536388 dated February 2016.
44. RWM Organisational Baseline Document. RWSP02 Rev 6, January 2016.
45. RWM Organisational Baseline Document Procedure. RWPR03 Rev 1, January 2016.
46. RWM Risk Management Framework. RWSP05.
47. RWM Audit and Risk Committee Terms of Reference. RWTR15.
48. RWM HSSSEQ Sub-Committee Terms of Reference. RWTR51.
49. RWM Terms of Reference for the RWM Board. RWTR01.
50. Environment Agency and Office for Nuclear Regulation letter to RWM. Organisational development: Findings from joint inspection, 8-10 February 2016. EA Ref GDF/T&O/2016/07 dated 14 April 2016 |










 Campaigners in 1995 Opposing the Nirex plan to dump low and intermediate level nuclear wastes in our geology. Images: 200 Campaigners Walking the Lake District Boundary Fault & The Trojan Horse (Nirex ‘exploratory boreholes’ preparing the way for Geological Dump) West Cumbria was ruled out as a site to bury nuclear waste 20 years ago because the geology was unsafe. The plan this time round is ten times as big and to include high level nuclear wastes, so not surprisingly Cumbria County Council said NO in January 2013.
Campaigners in 1995 Opposing the Nirex plan to dump low and intermediate level nuclear wastes in our geology. Images: 200 Campaigners Walking the Lake District Boundary Fault & The Trojan Horse (Nirex ‘exploratory boreholes’ preparing the way for Geological Dump) West Cumbria was ruled out as a site to bury nuclear waste 20 years ago because the geology was unsafe. The plan this time round is ten times as big and to include high level nuclear wastes, so not surprisingly Cumbria County Council said NO in January 2013.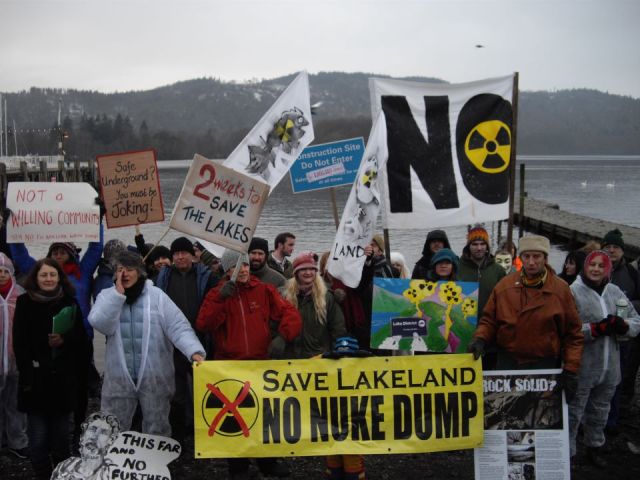 2012 Campaigners at Bowness Rally – No Geological Nuke Dump (intermediate AND high level nuclear wastes and 10 times bigger than the 1995 plan!) However, in order to build new nuclear plants the industry and government need to be seen to have a
2012 Campaigners at Bowness Rally – No Geological Nuke Dump (intermediate AND high level nuclear wastes and 10 times bigger than the 1995 plan!) However, in order to build new nuclear plants the industry and government need to be seen to have a