National Security
North Korea Designed A Nuke. So Did This Truck Driver
https://www.npr.org/2017/12/26/570806064/north-korea-designed-a-nuke-so-did-this-truck-driver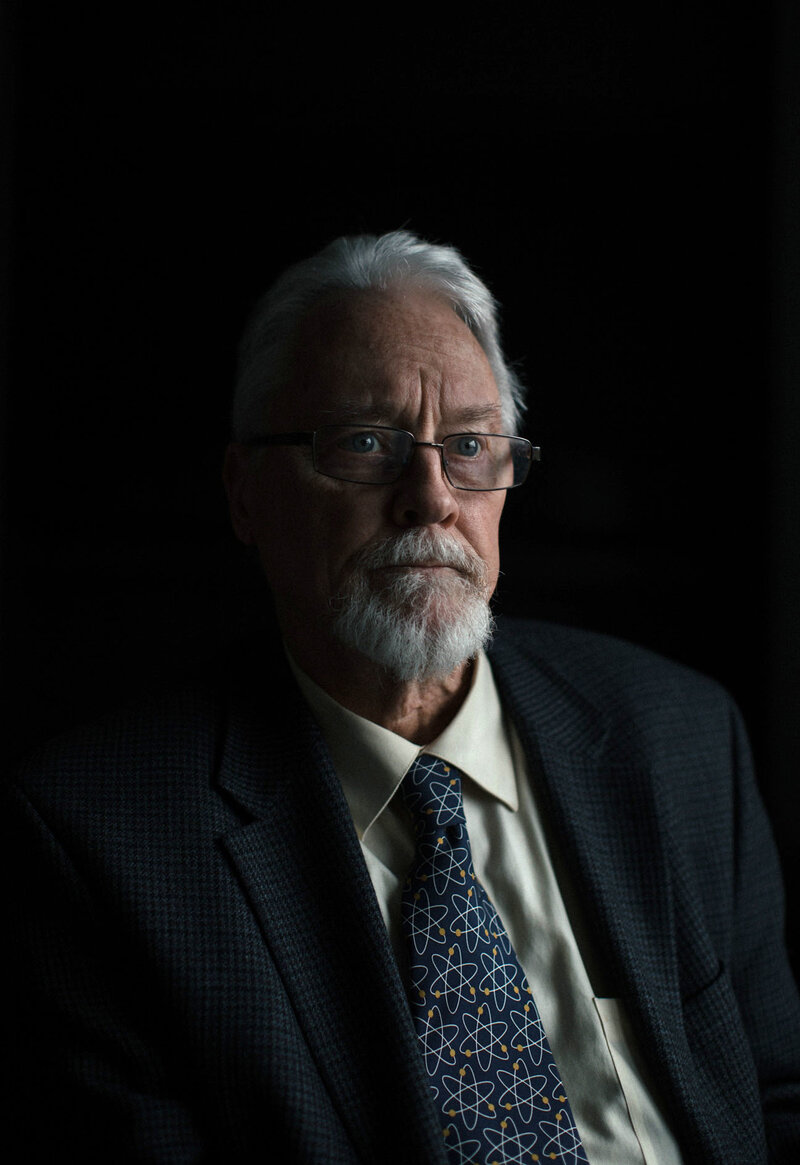
John Coster-Mullen has reverse-engineered America's first nuclear weapons and has self-published a book on his findings. Meredith Rizzo/NPR hide caption
toggle caption 
John Coster-Mullen has reverse-engineered America's first nuclear weapons and has self-published a book on his findings.
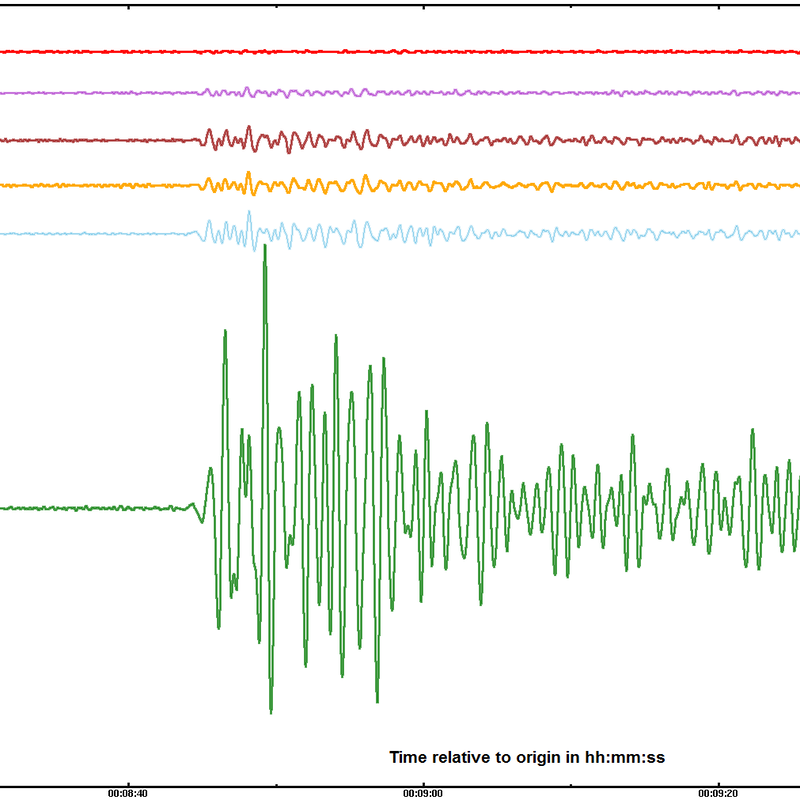
Meredith Rizzo/NPR The weapon was powerful; at least 10 times more destructive than the bomb the U.S. dropped on Hiroshima at the end of World War II. The North claimed it was an advanced, thermonuclear design. The test came just months after a report that some intelligence officials believed North Korea had successfully "miniaturized" some of its nukes in order to fit them on top of missiles.
The apparently rapid progress alarmed politicians and pundits, and it worried average Americans, many of whom hadn't thought much about nuclear weapons since the end of the Cold War.
But a 71-year-old truck driver named John Coster-Mullen wasn't surprised. Nuclear weapons are not particularly "hard" to design and build, he says. "Compared to what they do in manufacturing today for making a light bulb, these are simple. They really are," he says.
Coster-Mullen is an unlikely judge of North Korea's nuclear progress. He works nights for a major trucking firm, delivering merchandise to big box stores. Before that, he worked as a photographer. He never graduated from college.
But for the past 24 years, he has had an extraordinary hobby. He has carefully re-created detailed designs of America's very first nuclear weapons: Little Boy, the bomb that was dropped on Hiroshima, and Fat Man, the one that fell on Nagasaki.

The self-published Atom Bombs: The Top Secret Inside Story of Little Boy and Fat Man compiles research, drawings and archival photos of the Fat Man and Little Boy bombs. Meredith Rizzo/NPR hide caption
toggle caption 
The self-published Atom Bombs: The Top Secret Inside Story of Little Boy and Fat Man compiles research, drawings and archival photos of the Fat Man and Little Boy bombs.
Meredith Rizzo/NPR On the day we meet, Coster-Mullen is wearing a rumpled suit jacket with a patterned atomic tie. His unbroken way of speaking is cluttered with minute details of the bomb: The threading on Little Boy's nose cone (it was two threads per inch); the gold foil used at the center of the Fat Man design (physicists debated for hours about how many thin sheets to use).
It would be easy to write him off as an eccentric, but experts do not. "He knows a lot," says Johnpierre Paglione, a physics professor at the University of Maryland who recently invited Coster-Mullen to give a lecture about the bomb as part of his class on the Manhattan Project.
"The impressive thing about the work, to me, is how much information he was able to curate over time," says Jeffrey Lewis, a scholar at the Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey.
It all began in 1993 with a scheme to make a little money.
"The 50th anniversary of the bombs was coming up, and I thought I could make little replicas of the bombs and sell them," Coster-Mullen recalls.
To him it made sense. He'd grown up at the dawn of the Atomic Age and loved making models. He figured some like-minded baby boomer might buy them. Some companies were already making models of the bombs, but Coster-Mullen noticed their versions contained small errors in the tail design and elsewhere. He thought he could do better.
"I'm a perfectionist. I want everything where it should be," he says.

A 1965 image shows a replica of a Fat Man nuclear bomb, the type dropped on Nagasaki, Japan, in 1945, on view for the public in Los Alamos, N.M. AP hide caption
toggle caption 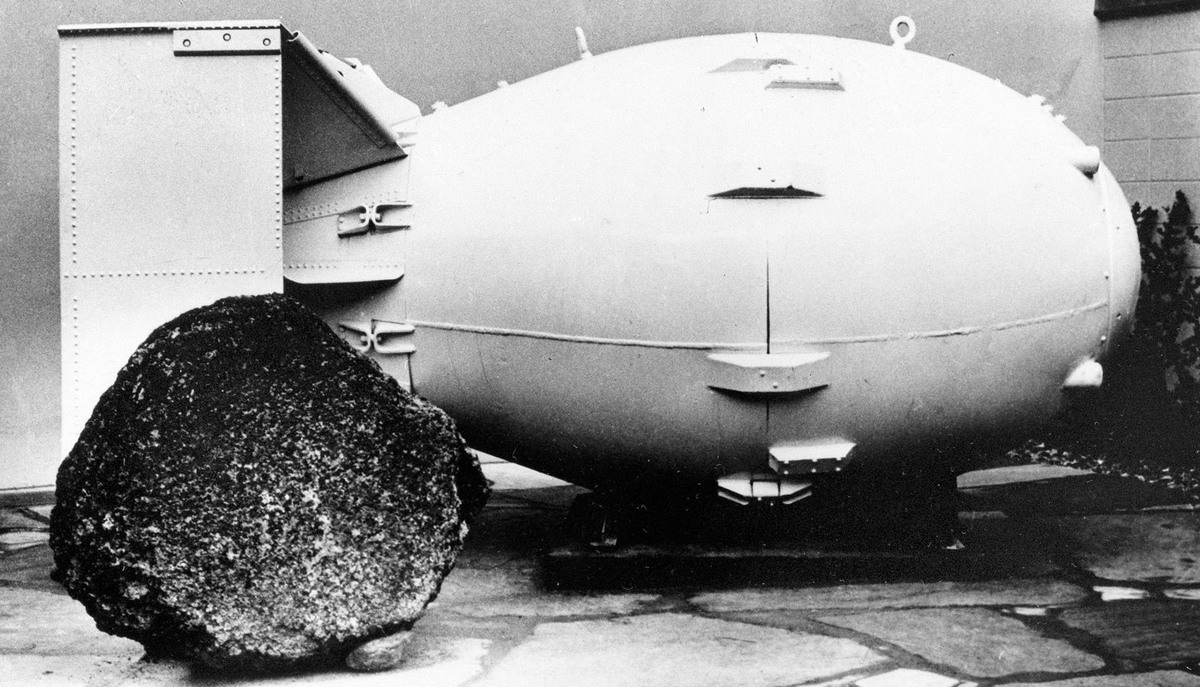
A 1965 image shows a replica of a Fat Man nuclear bomb, the type dropped on Nagasaki, Japan, in 1945, on view for the public in Los Alamos, N.M.
AP "The brochure turned into a 431-page book," he says.
Coster-Mullen never sold a single model, but he has been adding to his bomb brochure ever since, building up what are basically complete specs for America's first nuclear weapons. He has traveled the country, and the world, to glean all sorts of supposedly secret details.
"Nobody leaked anything to me,"he says. "I found all this information was hiding in plain sight."
Like the time he went to a lecture by someone who'd worked on the development of the bombs. At the end of the talk, the man held up a special commemorative paperweight, which had been made using a mold. "The mold they poured the plastic into was the same mold they poured the plutonium into to make the cores," says Coster-Mullen. The paperweight was a perfect copy of one hemisphere of a Fat Man-type bomb's nuclear core.
Coster-Mullen ran up after the lecture, made a few quick measurements and got what was once highly classified information.

On private land in the western U.S., Coster-Mullen found this fragment of what he believes is bomb casing from a test version of the Fat Man design. Meredith Rizzo/NPR hide caption
toggle caption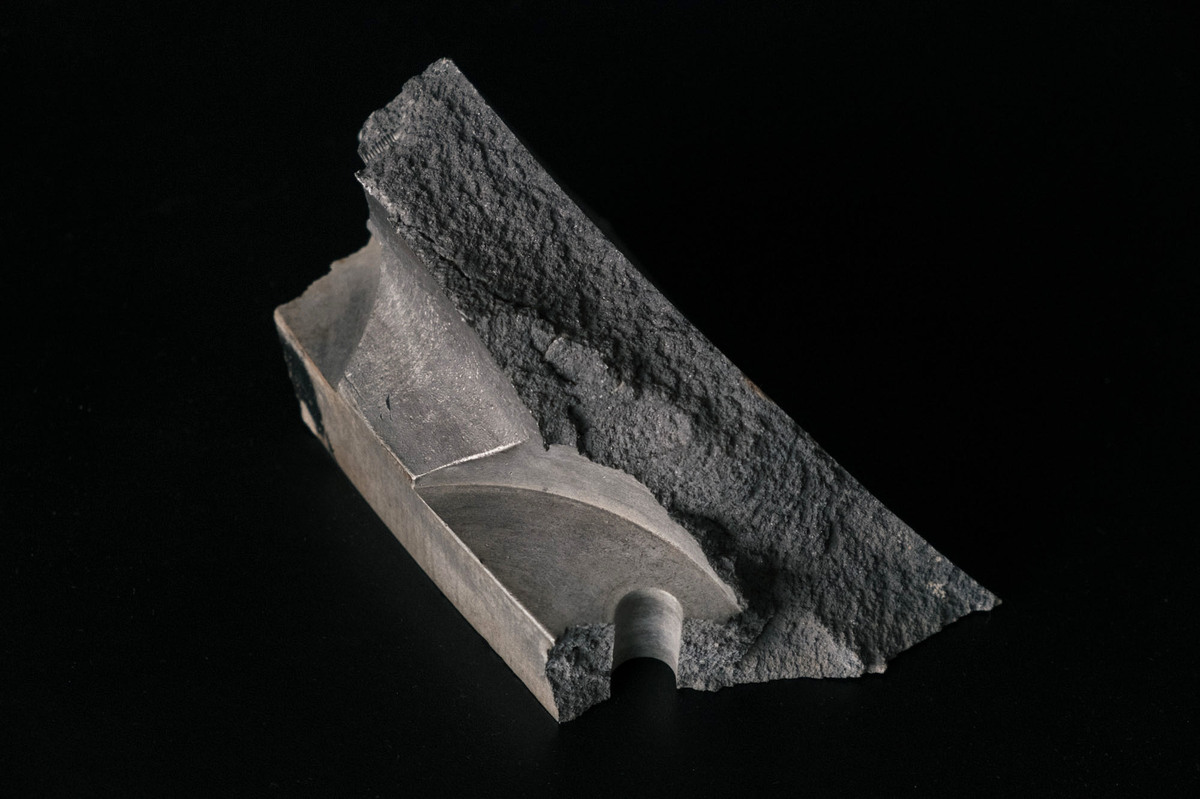 
On private land in the western U.S., Coster-Mullen found this fragment of what he believes is bomb casing from a test version of the Fat Man design.
Meredith Rizzo/NPR Public secrets
Coster-Mullen lives for those "Ah ha!" moments, and they've added up to a very complete diagram of each bomb. I tried to contact several former nuclear weapons designers about the accuracy of his work. None of them wanted to comment publicly on it.
But Alex Wellerstein, a historian at the Stevens Institute of Technology who specializes in nuclear weapons, says Coster-Mullen's work is the "gold standard." "His view of how the bombs worked is the most compelling I've seen," Wellerstein wrote in an email.
Lewis says Coster-Mullen's odyssey shows that nuclear weapons just aren't that hard to understand. "If a truck driver from Milwaukee can roughly replicate one, then that tells you that there is nothing mysterious about them," Lewis says.
"Anyone who thinks that ignorance is going to be an effective prohibition on a small nation attaining nuclear weapons should take heed of John's work," agrees Wellerstein. "There's more information out there than most people realize. And it has been out there for a long time."
In fact, many small nations have put together nuclear weapons designs over the years. In the 1940s and 1950s, Sweden had a bomb program that produced a complex design, Lewis says. Australia also is believed to have worked on a weapon design, as did Iraq under Saddam Hussein.
The real challenge is getting the uranium or plutonium needed to make the design a reality. "The hard part is creating the nuclear fuel. That requires a nation-state," Coster-Mullen says.
For all its limitations, North Korea is such a state. It has the reactors and centrifuges needed to make bomb-grade fuel.
In the end, Lewis says, the only way to halt North Korea's progress may be to somehow convince the country's leaders that it's in their best interest to stop it themselves. That seems to have worked in the case of Iran, where a nuclear program was frozen in exchange for sanctions relief and other financial incentives.
North Korea, which has already developed nuclear weapons, is a considerably more difficult case, Lewis concedes. But if nothing is done, he expects their progress to continue apace.
"I think we watch too many superhero movies; we imagine that we can physically prevent people from doing this," Lewis says. "But it is so easy."
National Security
NOEL KING, HOST:
This year, deep inside a mountain, North Korea detonated a giant nuclear bomb. It also launched missiles. And so for the first time since the Cold War ended, a lot of us ordinary Americans have started thinking about nuclear weapons. But one American, a big rig trucker, has been thinking about these weapons for decades, and he can't stop. NPR's Geoff Brumfiel has the story of his obsession with the bomb and what it can tell us about North Korea.
GEOFF BRUMFIEL, BYLINE: John Coster-Mullen is 71 years old and lives in Milwaukee. He works for a major trucking firm delivering merchandise to big-box stores.
JOHN COSTER-MULLEN: Twelve hours a night, five days one week and six days the next.
BRUMFIEL: But for the past 24 years, Coster-Mullen has had an extraordinary hobby. He has carefully recreated detailed designs of America's very first nuclear weapons - Little Boy, the bomb that was dropped on Hiroshima, and Fat Man, the one that fell on Nagasaki. It all began in 1993 with a scheme to make a little money.
COSTER-MULLEN: The 50th anniversary was coming up on the bombs, and maybe I could make little replicas of the bombs and sell them.
BRUMFIEL: To him, it made sense. He'd grown up at the dawn of the atomic age and loved making models. He figured some like-minded baby boomer might buy them. Now, some companies were already making models of the bombs, but Coster-Mullen noticed their versions looked off. Maybe the tailfins were wrong or something like that. He thought he could do better.
COSTER-MULLEN: If you're going to do it, do it real, and I'm a perfectionist. I want everything where it should be.
BRUMFIEL: So to make his models, he drove 1,300 miles to the birthplace of the atomic bombs - Los Alamos, N.M. The museum there has accurate, full-scale replicas of Little Boy and Fat Man he could work from. As he designed his models, he decided he'd write a little brochure to go with them.
COSTER-MULLEN: And the brochure turned into a 431-page book.
BRUMFIEL: Coster-Mullen never sold a single model, but he's been adding to his bomb brochure ever since, building up what are basically complete specs on America's first nuclear weapons. He's traveled the country and the world to glean all sorts of supposedly secret details.
COSTER-MULLEN: Nobody leaked anything to me. I found all this information was hiding in plain sight.
BRUMFIEL: Like the time he went to a lecture by someone who'd worked on the development of the bombs and the guy had the special commemorative paperweight.
COSTER-MULLEN: It turned out that paperweight, that souvenir, the mold they poured the plastic in, it was the same mold they poured the plutonium into to make the cores.
BRUMFIEL: The small, nuclear cores at the center of the Fat Man-type bombs. So Coster-Mullen ran up after the lecture, made a few quick measurements and got what was once highly classified information. He also spends a lot of time poring over declassified photographs and documents and thinking about how the pieces they describe fit together.
COSTER-MULLEN: I've had a lot of those aha moments where it suddenly hits you. And when I'm driving at night, I've had a lot of these where it flashes in your head and you're like, oh, oh, oh, oh, my.
BRUMFIEL: Coster-Mullen lives for those aha moments, and they've added up to a very complete diagram of each bomb. I ask him to show me his design for Fat Man.
COSTER-MULLEN: I used to know the page numbers, but when you keep adding stuff, the page numbers get moved around. OK, there we go.
BRUMFIEL: Coster-Mullen drew it himself. The level of detail is incredible.
COSTER-MULLEN: The central core is the 3.5, 3.6-inch diameter plutonium core. That's what they were trying to compress.
BRUMFIEL: Coster-Mullen sells his book on Amazon. I tried to contact several former nuclear weapons designers about his work. None of them wanted to comment publicly on it. But Jeffrey Lewis, a scholar at the Middlebury Institute of International Studies, says conversations he's had suggests the designs are reasonably close to the real thing.
JEFFREY LEWIS: I'm not in a position to judge, but I observe that people who are seem to take them seriously, and some of those people are alarmed.
BRUMFIEL: But Lewis has a little bit of a different take on this. He says Coster-Mullen's odyssey shows nuclear weapons just aren't that hard.
LEWIS: If a truck driver from Milwaukee can roughly replicate one, then that tells you that there is nothing mysterious about them.
BRUMFIEL: The only hard part is getting the uranium or plutonium to fuel the bomb, which brings us back to North Korea. It has both. Earlier this year, it conducted a massive nuclear test of a powerful weapon at least 10 times more destructive than the Hiroshima bomb. That led to a lot of talk about stopping North Korea from advancing its technology. But Lewis says that may not be possible.
LEWIS: I think we watch too many superhero movies. We imagine that we can physically prevent people from doing this, but it is so easy.
BRUMFIEL: That's why Lewis says the only way to halt North Korea's progress may be to somehow convince them that it's in their best interest to stop it themselves. Geoff Brumfiel, NPR News.
(SOUNDBITE OF APPALACHES' "PISOECOURSE")
This year, deep inside a mountain, North Korea detonated a giant nuclear bomb. It also launched missiles. And so for the first time since the Cold War ended, a lot of us ordinary Americans have started thinking about nuclear weapons. But one American, a big rig trucker, has been thinking about these weapons for decades, and he can't stop. NPR's Geoff Brumfiel has the story of his obsession with the bomb and what it can tell us about North Korea.
GEOFF BRUMFIEL, BYLINE: John Coster-Mullen is 71 years old and lives in Milwaukee. He works for a major trucking firm delivering merchandise to big-box stores.
JOHN COSTER-MULLEN: Twelve hours a night, five days one week and six days the next.
BRUMFIEL: But for the past 24 years, Coster-Mullen has had an extraordinary hobby. He has carefully recreated detailed designs of America's very first nuclear weapons - Little Boy, the bomb that was dropped on Hiroshima, and Fat Man, the one that fell on Nagasaki. It all began in 1993 with a scheme to make a little money.
COSTER-MULLEN: The 50th anniversary was coming up on the bombs, and maybe I could make little replicas of the bombs and sell them.
BRUMFIEL: To him, it made sense. He'd grown up at the dawn of the atomic age and loved making models. He figured some like-minded baby boomer might buy them. Now, some companies were already making models of the bombs, but Coster-Mullen noticed their versions looked off. Maybe the tailfins were wrong or something like that. He thought he could do better.
COSTER-MULLEN: If you're going to do it, do it real, and I'm a perfectionist. I want everything where it should be.
BRUMFIEL: So to make his models, he drove 1,300 miles to the birthplace of the atomic bombs - Los Alamos, N.M. The museum there has accurate, full-scale replicas of Little Boy and Fat Man he could work from. As he designed his models, he decided he'd write a little brochure to go with them.
COSTER-MULLEN: And the brochure turned into a 431-page book.
BRUMFIEL: Coster-Mullen never sold a single model, but he's been adding to his bomb brochure ever since, building up what are basically complete specs on America's first nuclear weapons. He's traveled the country and the world to glean all sorts of supposedly secret details.
COSTER-MULLEN: Nobody leaked anything to me. I found all this information was hiding in plain sight.
BRUMFIEL: Like the time he went to a lecture by someone who'd worked on the development of the bombs and the guy had the special commemorative paperweight.
COSTER-MULLEN: It turned out that paperweight, that souvenir, the mold they poured the plastic in, it was the same mold they poured the plutonium into to make the cores.
BRUMFIEL: The small, nuclear cores at the center of the Fat Man-type bombs. So Coster-Mullen ran up after the lecture, made a few quick measurements and got what was once highly classified information. He also spends a lot of time poring over declassified photographs and documents and thinking about how the pieces they describe fit together.
COSTER-MULLEN: I've had a lot of those aha moments where it suddenly hits you. And when I'm driving at night, I've had a lot of these where it flashes in your head and you're like, oh, oh, oh, oh, my.
BRUMFIEL: Coster-Mullen lives for those aha moments, and they've added up to a very complete diagram of each bomb. I ask him to show me his design for Fat Man.
COSTER-MULLEN: I used to know the page numbers, but when you keep adding stuff, the page numbers get moved around. OK, there we go.
BRUMFIEL: Coster-Mullen drew it himself. The level of detail is incredible.
COSTER-MULLEN: The central core is the 3.5, 3.6-inch diameter plutonium core. That's what they were trying to compress.
BRUMFIEL: Coster-Mullen sells his book on Amazon. I tried to contact several former nuclear weapons designers about his work. None of them wanted to comment publicly on it. But Jeffrey Lewis, a scholar at the Middlebury Institute of International Studies, says conversations he's had suggests the designs are reasonably close to the real thing.
JEFFREY LEWIS: I'm not in a position to judge, but I observe that people who are seem to take them seriously, and some of those people are alarmed.
BRUMFIEL: But Lewis has a little bit of a different take on this. He says Coster-Mullen's odyssey shows nuclear weapons just aren't that hard.
LEWIS: If a truck driver from Milwaukee can roughly replicate one, then that tells you that there is nothing mysterious about them.
BRUMFIEL: The only hard part is getting the uranium or plutonium to fuel the bomb, which brings us back to North Korea. It has both. Earlier this year, it conducted a massive nuclear test of a powerful weapon at least 10 times more destructive than the Hiroshima bomb. That led to a lot of talk about stopping North Korea from advancing its technology. But Lewis says that may not be possible.
LEWIS: I think we watch too many superhero movies. We imagine that we can physically prevent people from doing this, but it is so easy.
BRUMFIEL: That's why Lewis says the only way to halt North Korea's progress may be to somehow convince them that it's in their best interest to stop it themselves. Geoff Brumfiel, NPR News.
(SOUNDBITE OF APPALACHES' "PISOECOURSE")
Copyright © 2017 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by Verb8tm, Inc., an NPR contractor, and produced using a proprietary transcription process developed with NPR. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.